Mark this very moment you stop looking for the SEO checklist that will help you increase your site’s organic traffic and rank on Google. You’ve found it!
We’ve compiled the ultimate checklist for driving SEO success, covering the best practice points and tasks that you should be aware of. You can use this article as your go-to resource for everything from SEO basics to must-knows when analyzing off-page signals.
We’ve divided this checklist into sections that cover the main SEO focus areas:
- SEO Basics
- Keyword Research
- Mobile SEO
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Content
- Local SEO Tips
- Special Google Algorithm Rules
- Brand Signals
- Social Media Tips
- User Interaction
For a comprehensive SEO strategy, you must focus on all of the above. It’s not every day you bump into these potential keys to your business’ breakthrough. Seize the chance now and follow our checklist to ensure you’re adhering to SEO best practices in each area.
SEO Basics Checklist
Still trying to figure out what SEO is? It stands for Search Engine Optimization. Search Engine Optimization is the practice of tailoring your website in a manner that attracts more traffic from people browsing the web through a search engine. If you don’t cover the fundamentals, your site may find it difficult to rank for competitive terms.
1. Set Up Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an essential tool that provides you with invaluable insights into your site’s performance as well as a wealth of data that you can use to grow your site’s organic visibility and traffic.
Search Console is designed to help you track your site’s performance in Google search.
That’s why it’s packed with useful features, like:
- See which keywords bring you the most traffic
- Submit your sitemap
- Google doesn’t always know ALL the pages but this tells Google where everything is that you want them to find
- Fix website errors
- See your page experience scores
2. Install Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing Webmaster Tools is Microsoft’s equivalent platform, providing data and insights for their search engine.
These vital tools enable you to view the search terms and keywords for which users are finding your site on the SERPs, submit sitemaps, identify crawl errors, and much more.
Is Bing as popular as Google? No. But Bing gets approximately 1 billion visitors per month. So it’s worth optimizing for.
Plus, Bing Webmaster Tools has some nifty features, like a built-in keyword research tool.
3. Set Up Google Analytics
You can’t make good decisions unless you have the right data.
Google Analytics is a free marketing analytics tool that lets you see data and insights about how many people visit your site, who they are, and how they interact with it.
You will also need to connect Google Analytics and Google Search Console to import data from the latter.
4. Install and Configure an SEO Plugin (If You’re Using WordPress)
If you use WordPress as your CMS (Content Management System) (which you should, given that it now powers 39.5 percent of the web), you must install and configure an SEO plugin to provide the functionality and features you need to properly optimize your site.
You may refer to this blog by Semrush, 2020, for the WordPress SEO Checklist Guidelines.
If you are using a CMS other than WordPress, consult with your developer to see if you need to install a dedicated SEO plugin or module or if the features you require are included out of the box.
5. Generate and Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap’s purpose is to assist search engines in determining which pages should be crawled and which is the canonical version of each. It is simply a list of URLs that specify your site’s main content in order for it to be crawled and indexed.
Google supports a number of different sitemap formats, but XML is the most commonly used. You will usually find your site’s sitemap at https://www.domain.com/sitemap.xml.
If you’re using WordPress and one of the above-mentioned plugins, generating a sitemap is standard functionality.
Otherwise, you can use one of the many sitemap generator tools available to create an XML sitemap. In fact, we recently updated our ultimate sitemaps guide, which includes our top recommendations.
After you’ve created your sitemap, make sure to submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
6. Create a Robots.txt File
Simply put, your site’s robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages and files they can and cannot demand from your site.
It is most commonly used to prevent specific sections of your site from being crawled and is not intended to be used to de-index a webpage and prevent it from appearing on Google.
The robots.txt file for your website can be found at https://www.domain.com/robots.txt.
Check to see if you already have one.
If you don’t have one, you should make one—even if you don’t need to prevent any web pages from being crawled right now.
Several WordPress SEO plugins allow users to create and edit their robots.txt file, but if you’re using a different CMS, you may need to create the file manually in a text editor and upload it to the root of your domain.
7. Install Yoast SEO (WordPress Users Only)
Yoast is the most widely used SEO plugin on the internet.
With good reason.
Yoast makes optimizing your WordPress site for search engines a breeze.
8. Check Search Console for Manual Actions
In rare cases, you may discover that having a manual action imposed on your site has had a negative impact on it.
Manual actions are typically the result of a clear attempt to violate or manipulate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines—this includes user-generated spam, structured data issues, unnatural links (both to and from your site), thin content, hidden text, and even pure spam.
Most sites will never be affected by a manual action.
However, you can look for these in Google Search Console’s manual actions tab. If your site has received a manual action, you will be notified, but if you are working on a new project or taking over a site, it should always be one of the first things you check.
9. Make Sure That Google Can Actually Index Your Website
Making sure your site can be indexed by Google is part of having your SEO basics covered. You can use the Site Audit Tool to ensure that your website can actually be crawled and indexed.
Organize a Site Audit for your project. After completing the audit, you can access the Crawlability report for more information.
10. Use Video & Optimize It
Video is more valuable than ever. Don’t let a lack of funds prevent you from participating. There are numerous options available to you, including phone recordings and motion graphics
11. Pay Attention to User Intent
When conducting keyword research, combine user intent search queries with voice search queries, such as questions, to help support those user intent queries.
12. Begin establishing your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness
It will be difficult for a newcomer to compete with a website that has been around for ten years.
There is only one place to begin: creating excellent content and pages that highlight your expertise (whether you are an individual or a business).
That content should help you achieve your SEO and business objectives.
13. Make Your Content Easy to Use
Ultimately, SEO is about people.
Furthermore, the majority of search engine updates favor user-friendly content.
In addition to the technical aspects of SEO, learn about personas, human behaviors, and user trends in order to get the most traffic out of SEO.
14. Customer testimonials continue to be extremely popular
Make a plan to solicit product reviews or comments from customers. These are used by search engines to attribute value, resulting in higher conversions.
15. Consider SEO from the star
Bring in an SEO professional early in the process when redesigning your website.
Design trends should be tailored to SEO best practices, particularly for the site’s mobile version.
16. Manage Client Expectations Honestly
This industry is full of shady characters.
Failure to meet expectations can give the impression that you are one of them.
17. Consider Keywords Other Than ‘Exact Match’
It is not necessary to use exact match keyword terms.
Google comprehends entities (things and concepts) as well as relationships.
It is capable of associating your topical keyword search terms.
18. Use a Referral
Personalize your calls-to-action in response to a referral.
This can also be done based on your location and keyword search query.
19. Pick a Short Domain
When selecting a domain name, keep it to 15 characters or less.
People find it easier to remember shorter domain names.
20. Find All Variations of Your Sit
When searching for your site in search engines using’site:example.com,’ make sure to find all variations of your site. While not everyone still uses www. And in most cases httpS is forced, it is still best practice to ensure all variations work.
For instance, look up the following:
http://example.com
http://www.example.com
https://example.com
https://www.example.com
Keyword Research Checklist
Keyword research is known as the foundation of SEO. It will be difficult to rank for the right terms without a solid keyword research process. If you aren’t ranking for the right terms, your traffic won’t convert as well as it could. In this section, we’ll show you how to quickly find keywords that your customers search for in this checklist.
21. Search based on a seed keyword
This approach, as the name implies, begins with a seed keyword. Any sentence that describes the issue will suffice.
Simply type the keyword “coffee machines” into the tool to create content about coffee machines.
Note: When talking about keyword research tools, I’m using KWFinder as an example tool in this guide. It supports both seed keyword and competitor keyword research.
22. Identify Your Competitors
Finding the terms that are working for your competitors is one of the quickest ways to get started with keyword research.
There is no such thing as wasted time when it comes to competitor analysis.
Run your own domain (as well as the domains of your key competitors) through the Semrush Domain Overview tool to quickly identify those competitors who are competing in the same space as you and how your visibility compares.
23. Check your competitor’s domain to get new topic ideas
By researching the keywords that your competitors rank for, you might come up with unique and engaging topic ideas for your website.
In the following example, I’ve entered the domain of a prominent coffee blog, homegrounds.co into Semrush’s Domain Overview Tool for example. The tool displays a list of hundreds of keywords for which this website ranks.
It’s really that simple.
24. Find Your Main “Money” Keywords
You must be aware of your primary “money” keywords. If you haven’t already guessed, these are the ones that will drive you leads, sales, and conversions.
You will also find these referred to as head terms and pillar page keywords. In general, these are the high volume, high competition keywords that best summarize what you have to offer, either at the topic or category level.
25. Discover Long Tail Keywords With “Google Suggest”
This is one of the most effective methods for locating long tail keywords.
This is how it works:
To begin, enter a keyword into Google. But don’t hit the enter key… or the “Google Search” button. Instead, look at the keywords that Google suggests. Because these keywords are pulled directly from Google, you understand that people are looking for them. This means they make excellent keywords for optimizing your website.
Check out keywordtool.io for more information. This tool scrapes Google Suggest keywords, making scaling this process much easier.
26. Find Solid Keywords In The Google Keyword Planner
The Google Keyword Planner is Google’s official keyword research tool. It is technically intended for use with Google Ads. Having said that, it is still extremely useful for SEO keyword research.
After all, the information comes directly from Google. So, you know it’s very accurate.
27. Create a Keyword Map
Once you’ve identified your target keywords, you’ll need to “map” or pair them with pages on your site, as well as identify any gaps. Here’s Semrush’s guide to keyword mapping.
It’s critical that you invest the time necessary to ensure that you’re targeting the right pages with the right keywords, and the process outlined in the guide can assist you in getting this right the first time and using it to power your strategy.
28. Analyze the Intent of Pages That Rank
This requires spending time analyzing the pages that rank for your target terms and ensuring that your content is consistent. You must ensure that the content of your page corresponds to the searcher’s intent. You won’t be able to ensure that your content aligns with Google’s if you don’t understand the intent of the content that Google is ranking.
29. Identify Questions That Are Being Asked
Knowing what questions your audience is asking can help you better answer them through the content on your website.
Using the Keyword Magic Tool, you can generate a list of related questions for any keyword. To see results, enter a keyword and set the filter to “questions.”
This is a great place to start and can provide a lot of inspiration, especially if you start with more specific keywords.
30. Understand How Difficult It Is to Rank for Your Target Keywords
Until a new website gains authority, it may struggle to rank for competitive keywords.
As a result, you must assess the difficulty of the keywords you intend to target. When you begin your SEO strategy, this can help you manage your own (or your client’s) expectations.
Head to a tool like the Keyword Overview Tool (any tool that shows keyword difficulty will do), input your target keywords to see the keyword difficulty; this is how difficult it will be for a new website to rank on the first page.
31. Tap Into Online Communities
Keywords can be found in abundance on Reddit, Quora, forums, and other online communities.
32. Check keywords with high impressions but low number of clicks
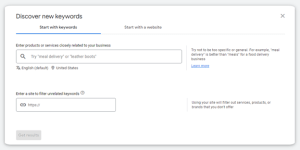
Google Ads Planner to see Search Volume vs. Competition.
Using search tools such as the Google Ads Keyword Planner, you are able to find high to low performing keywords relevant to your industry.
In searching through these terms, you’re looking for keywords with high impressions but low clicks or engagement rate because these are keywords that a lot of people are interested in, but none of the competition has written compelling SEO content that draws in customers.
This is where you can come in and write content that converts searchers.
33. Identify Low Competition Keywords With KWFinder
KWFinder is a keyword research tool that is available for free.
What distinguishes KWFinder is that it provides a plethora of data on each keyword.
As you can see, when you enter a keyword into KWFinder, you will receive information on:
- The number of searches
- Difficulty of Keyword
- CPC
- Trends
- Visits predicted
This allows you to select low-competition keywords that are simple to rank for.
34. Find “Question Keywords” With “Answer The Public”
Question keywords are exactly what you need for blog posts and articles. And you can easily find them with Answer The Public. This free tool shows you questions that people search for online.
35. Examine Exit Pages
Analyze the exit pages to see which pages users are leaving your site from.
Why are users abandoning the site?
If users are leaving without making any conversions, consider revising these exit pages in order to increase time spent on the site.
36. Add Your IP Address To Not Get Dummy Data In Your Analytics (OR at least exclude admin traffic)
Google Analytics should have your IP address and filter it out from the data. You might hit your home page 40 times in a month and provide false information to Google Analytics.
At a minimum, plugins like SEO PRESS will allow you to exclude editor, admin, etc. traffic so that you are getting an accurate read and optimizations for your website. Since everyone is working remotely, we suggested excluding specific User role traffic since it will tend to be more accurate.
37. Watch Out for Traffic Drops
If your traffic suddenly drops, it could be due to an algorithm change – or a manual action.
Check your email and Google Search Console to see if a manual action notification was sent to you.
38. Configure Google Ads for Store Visits Conversions.
If you are eligible, configure your google ads account to record store visits as conversions.
39. GSC: Include both the www and non-www versions of your site.
Are you just getting started with Google Search Console? Don’t forget to include both versions of your website.
You should include both the www and non-www versions of your website so that Google can better keep an eye on your site.
Set the preferred location once it’s completed.
40. GSC: Add Your Subdomains
If you have multiple subdomains, you should add them to Google Search Console as new properties to get all of the data out of them that you can.
41. Change Your Meta Descriptions
Consider rewriting your meta descriptions if you see low click-through rates in the Google Search Console Search Analytics report.
42. Create Custom Dashboards
Create custom dashboards in Google Analytics or Google Data Studio to save time.
These custom reports can auto update, so as soon as you log in, you’ll be able to see exactly what you need to see.
43. Without Insights, Data Is Just Numbers
Never optimize without first considering the context of your analytics.
Use content analytics tools to assess opportunities and gain a better understanding of trends and behaviors.
Mobile SEO Checklist
44. Take a ‘Mobile-First’ Approac
Google switched to Mobile First Indexing for all sites in September 2020.
To see how Google’s mobile search agent sees your site, use the Mobile-Friendly Test Tool in Google Search Console.
45. Investigate Whether AMP & PWA Are Right for You
Launch Google Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) or Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) to help prepare for the mobile-first index and increase mobile search traffic.
If you don’t have a mobile site, Google will serve up your AMP pages or PWAs in the mobile-first index, so make sure your primary content and links are listed on the AMP pages or PWAs.
46. Remove Interstitial
Remove pop-ups and interstitials from mobile unless they are required for age restrictions or data privacy.
Pop-ups can be replaced with many more effective methods.
47. Use Scroll Tracking on AMP
Scroll Tracking can be used with Google AMP and Google Tag Manager. It can be used to see who is paying attention on your site and who is just a bounce.
48. Add Forms to AM
Even if Google AMP pages appear to be bare bones, forms can be added to capture leads.
49. B2C? Consider PWA
Consider investing in a Progressive Web App for B2C brands (PWA).
PWAs are expected to replace 50% of consumer-facing apps.
Starbucks, Spotify, and Uber have already created memorable experiences, and customers will expect the same from smaller brands.
50. Use Breadcrumb Navigation on Your Mobile Websit
You want to show a clean destination path because it may help increase your mobile click-through rate.
Technical SEO Checklist
Your rankings can be made or broken by technical SEO. Fortunately, resolving technical SEO issues isn’t that difficult… especially if you stick to the items on this checklist.
Here are some of the most common technical best practices to remember.
51. Make Sure You Are Using HTTPS
Since 2014, HTTPS has been recognized as a ranking factor. There’s no reason not to use HTTPS encryption on your website, and if you’re still using HTTP, it’s time to upgrade.
You can easily verify that your site is HTTPS by looking at the URL bar in your browser. You are using HTTPS if you see a padlock to the left of the URL.
52. Canonical Tags Don’t Save Crawl Budget
Search engines must crawl the duplicates as well to determine if they are indeed duplicates.
53. News + BERT = Top Stories Carousels
Google BERT now includes a top news carousel for news publishers.
Publishing legitimate news content, having AMP pages, and submitting your site to Google News are the best ways to appear in these results.
54. Use rel=canonical
Make sure that all of your pages that can be accessed via multiple URLs have the rel=canonical tag, which directs search engines to the main page.
When another site scrapes your content, the rel=canonical tags reduce confusion, and prevent duplicate content. You can find out more about rel=canonical tags at Moz.com.
55. Check to See If Your Pages Are Indexe
With a site: domain name search, double-check that your money pages are indexed. SEO Press has a convenient Instant Indexing feature.
Check to see if you’re double-indexed as well. Duplicate content can result from double-indexing.
56. Add Image Alt Attributes Before Posting
To compete with other sources, Google is shifting to a more visual search. Adding related images (and alt texts for those images) can improve the likelihood you end up on the front page of a search.
57. You Can Have Multiple Sitemaps
Create separate sitemaps for images, videos, profiles, and blog posts if you want Google to direct its crawl attention to specific sections of your site.
58. Get a Handle on Your URL Parameters
If your URLs are dynamic (e.g., www.donutsaregoodforyou.com/?mode=1-list=1), you’ll need to adjust your parameters in Google Search Console to reflect how you want Google to crawl your content.
Again, this aids in the reduction of duplicate content.
59. When using images, try to obtain images in vector format
These files scale better, resulting in higher image quality across multiple devices.
If you’re having trouble with page speed, consider switching to WebP files.
60. Use a CDN
Consider having your images hosted by a content delivery network (CDN).
A CDN can help your website load faster.
61. Use Canonical Tags for Similar Products
Instead of redirecting products with very similar descriptions and names, use the canonical tag.
62. Get Dedicated Hosting
While a privately hosted domain will not affect your search rankings, shared hosting may cause your site to be indexed less frequently.
Search engines index based on IP address, and when multiple IP addresses are used, search engines may receive too many signals.
63. Invest in Visual Search
Visual search should be incorporated into retail and e-commerce marketing strategies.
Amazon, Snapchat, and Bing have all added visual search to their platforms, so it’s worth the investment.
64. Utilize Structured Data
Getting to the first page of the SERPs isn’t as easy as it once was. But that’s not necessarily a bad thing.
There are numerous ways to tell Google you have valuable information that searchers want, including the Knowledge Graph, featured snippet, top stories, and video carousel.
So, to improve your chances, use structured data.
65. Examine Google’s Index for Duplicate Versions of Your Website
It is critical that you should only allow Google to index one version of your site.
These are different versions of your website that must all point to the same one.
It is up to you whether to use a non-www or www version, but the most common is https://www.domain.com.
All other versions should 301 redirect to the primary one, which you can test by typing each variant into your browser’s address bar.
Once you’ve established redirects without issue but are still able to access different versions, implement redirects as soon as possible.
66. Find and Fix Crawl Errors
A “Crawl Error” indicates that Google is having difficulty viewing a page on your website.
And if they are unable to view your page, it will not rank for anything. Through Google Search Console, you can quickly identify any crawl errors.
When you open the Coverage Report, you’ll see both errors and excluded pages, as well as those with warnings and those that aren’t valid.
Consider taking the time to correct any inconsistencies you find and investigate the cause of excluded URLs in greater depth. Issues such as 404 errors and incorrectly canonicalized pages may appear here, and these types of issues can have a negative impact on the performance of your website.
If you notice Google having difficulty accessing one of your important web pages (for example, robots.txt is blocking search engine spiders), you should fix it as soon as possible.
67. Improve Your Site Speed
Slow websites provide a poor user experience.
In fact, Google confirmed that page experience would become an even more important ranking factor in 2021. You must ensure that your site loads quickly and recognize that users continue to expect more.
To assess page performance and Core Web Vitals statistics, use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool.
68. Fix Any broken Internal and External Links
Another sign of a poor user experience is broken links. Nobody wants to click a link and discover that it does not take them to the expected page.
Your Site Audit report will contain a list of broken internal links, which you should fix by either updating the target URL or removing the link.
69. Find Out How Google Views Your Page
If Google is unable to fully access your page, it will not rank. That is why I suggest using the “Inspect URL” feature of Google Search Console.
Simply enter a page from your website into the GSC at the top.
70. Find and Fix HTTP Links on HTTPS Pages
Although most websites migrated from HTTP to HTTPS quite some time ago, it is still common to find internal links that point to HTTP pages rather than the current version.
Even if a redirect is in place to direct users to the new page, these are unnecessary and should be updated as soon as possible.
Look at the HTTPS Report in Site Audit to see if there are any issues.
If there are only a few broken links, you can manually update them in your CMS. If these are site-wide (as they frequently are), you must update page templates or perform a search and replace on the database.
71. Make Sure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
Google has recently introduced a new “Mobile-First Index.”
That is to say:
Your site will not rank well if it is not mobile optimized.
Fortunately, Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test makes it simple to assess your site’s mobile friendliness.
Simply enter a page from your website… and you’ll get a clear “yes or no” response.
72. Use an SEO-Friendly URL Structure
An SEO-friendly URL structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your pages. Users will appreciate it if your page URLs are short and descriptive.
Here’s an example of a URL that is SEO-friendly:

In contrast to a non-descriptive query string:
https://www.domain.com/category.php?id=32
To separate words in URLs, use hyphens rather than underscores.
Keep URLs as brief as possible (a study by Backlinko showed that shorter URLs tend to rank higher).
73. Include Structured Data
Structured data makes your organic listings stand out on the SERPs, and the example below shows both the review stars and the price, which improves the result.

Structured data markup is becoming increasingly valuable as Google continues to expand to more semantic data.
You should be using structured data if you aren’t already.
The Schema.org vocabulary, in fact, includes formats for structuring data for people, places, organizations, local businesses, reviews, and much more.
74. Check the Page Depth of Your Site
Pages should preferably be no more than three clicks deep in your site.
If they are, it is a sign that you need to spend some time reworking your site structure in order to flatten it. The deeper a page is in your website’s structure, the less likely it is that users or search engines will find it.
The “crawl depth,” or the number of clicks required to reach a page, can be found in the Site Audit tool’s Internal Linking report.
75. Check Temporary 302 Redirects
302 redirects indicate a temporary redirect, whereas 301 redirects indicate a permanent move. While Google has confirmed that 302s pass PageRank, the fact remains that if a 302 redirect isn’t expected to be removed at any point in the future, it should be updated to a 301.
Any 302 redirects will be clearly highlighted in the Site Audit report as pages with temporary redirects.
76. Find and Fix Redirect Chains and Loops
Redirects should not be used to send users or search engines through multiple redirects (a redirect chain), nor should they be used to create a loop.
Simply put, redirects should take you from page A to page B.
The Issues tab in Site Audit will highlight any issues with redirect chains and loops. You can fix these problems by updating all redirects in a chain to point to the final destination, or by removing and updating the redirect that is causing the loop.
On-Page SEO Checklist
It’s now time to optimize your content with a few tried-and-true on-page SEO techniques.
77. Include Your Keyword In Your URL
Your URL assists Google in determining the purpose of your page. Furthermore, a keyword-rich URL can boost your organic CTR.
For example, the target keyword for this page is “SEO checklist”.
So this is a perfect URL: backlinko.com/seo-checklist.
Simple.
78. Use Short URLs
Make your URLs as brief as possible.
Why?
According to a recent analysis of 11.8 million Google search results, short URLs rank highest in Google.
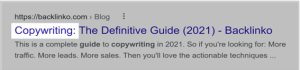
79. Front-Load Your Keyword In Your Title Tag
It goes without saying that you should include your keyword in your title tag. However, not everyone realizes that WHERE you place your keyword is important.
Specifically, you should place your keyword near the beginning of your title tag whenever possible.
Suppose you are writing for a blog post about Copywriting, here’s an example of a good title tag with that keyword:
80. Find and Fix Duplicate, Missing, and Truncated Title Tags
Title tags tell search engines what a page is about and influence whether or not a user clicks on it.
Avoid duplicate title tags—ideally, your site should not have duplicate content, and title tags should be specific enough that users can tell what type of page they’re about to land on.
Also, avoid using title tags that are too long, as they may be cut off in SERPs (you will see three dots after the title tag and part of it missing). Title tags with more than 70 characters are usually cut off.
You must also ensure that no title tags are missing (where the title tag is blank).
All of these issues are flagged in the Site Audit report’s Issues section and can be resolved by updating and improving your page’s title tags.
81. Embed Title Tag Modifiers
Title Tag Modifiers are words and phrases that you can include in your title tag. When you do this, your page can rank for a variety of long-tail keywords.
82. Use Your Keyword Once In The First 150 Words
Google prioritizes the first 100-150 words of your page. So make sure you use your keyword at least once here.
83. Locate and Correct Duplicate and Missing Meta Descriptions
Simply put, your meta description is what encourages a user to click on your listing over someone else’s, and it can have an impact on your organic click-through rate, either positively or negatively (CTR).
If you don’t have a meta description, Google will display a portion of your page’s content, which may include navigation text and other elements that look out of place in a search page. If you have duplicates, it’s likely that you’re not providing a unique description that encourages clicks.
84. Find and Fix Multiple H1 Tags
The H1 tag on a page represents the main heading of your content, and only one should be used per page.
Site Audit’s Issues tab will highlight pages with more than one H1 tag, and you should take the time to resolve these so that only one exists on each page.
The most common reason for multiple H1 tags is that your site’s logo, as well as the main heading on the page, is wrapped in one.
H1 tags should include a page’s primary target keyword, so make sure you’re tagging the right content.
85. Improve Title Tags, Meta Tags, and Page Content
If you don’t properly optimize your page titles and meta tags, you’re passing up an opportunity to rank not only for your primary keywords, but also for keyword variations.
Go to Google Search Console’s performance report and look for keywords on each page that have a high number of impressions but low clicks and a low average position.
This typically indicates that your page is deemed relevant for the queries and is ranking in some capacity, but you have not optimized the page by including these variations in your content or tags.
Remember that simply including keyword mentions will have little effect. Consider these extra keywords to be topics for additional H2s or subsections.
86. Run a Content Audit and Prune Content
A content audit is a useful way to determine what content is performing well and what content is not adding value.
Essentially, this means getting rid of content that doesn’t rank, doesn’t add value, and shouldn’t be on your site in the first place.
If a piece of content isn’t adding value to your site, it should be removed. It’s as simple as that. Kevin Indig’s guide to using Semrush for SEO pruning is a great place to start and will provide you with the knowledge you need to complete this process effectively.
You can also use our Content Audit tool to determine which pages to rewrite, remove, or update based on how the content is performing.
87. Optimize Images
Always keep image optimization in mind. It is an area of SEO that is frequently overlooked, from properly naming images with a descriptive file naming convention to optimizing the size and quality.
Unfortunately, Google can’t “see” images in the same way that humans can. You should optimize your image alt tags and filenames to help them understand your images.
To begin, when saving the image, use a filename that briefly describes what the image is. Then, when you add the image to your page, give it a descriptive alt tag.
88. Always do video optimization
In addition to photographs, you may include videos on your page. Because it combines aural and visual senses, video is one of the most popular media or content for consuming information online. Including videos in your material will engage your readers and lengthen their stay on your page.
When optimizing your video material, keep the following in mind:
- Your video’s title should be brief, entertaining, and include your major keyword.
- Include a detailed description of your video that describes the subject matter or what your visitors can expect to see. In the description, don’t forget to include your keywords and LSI keywords.
- Select high-quality, relevant thumbnails.
- If feasible, add subtitles to make it more user-friendly.
- Make sure your video is related to the rest of your material.
Including a video on your website increases viewer engagement and helps them better understand your material.
89. Improve Internal Linking
Internal links are one of the most underutilized link building strategies in SEO marketing. Spending time improving your site’s internal linking strategy can yield immediate results.
Some marketers believe that adding just one or two internal links from authoritative pages on your site can yield quick results.
Refer to this guide to executing an internal links strategy that works and begin to identify pages that need to be linked to from other pages.
A list of pages with only one internal link pointing to them can be found in the “Notices” section of the Site Audit Internal Linking report.
90. Find and Fix Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on the same site rank for the same keywords, causing them to compete with one another.
Assume you have two pages ranking for the term “SEO checklist”—one old, out-of-date page and one new, useful page. If Google favors the older page, it may decline to rank the newer, more useful page. In this case, combining the two pages would be a good idea to avoid dividing traffic.
Essentially, if your site is cannibalized, you will struggle to rank for competitive terms because search engines have difficulty determining which page to show.
Set up a Position Tracking campaign and check the Cannibalization tab to see if your site has keyword cannibalization issues.
This cannibalization guide walks you through the most common ways to find and fix these issues.
91. Find and Fix Orphaned Site Pages
Every page on your website should be linked to by at least one other page.
After all, if Google is unable to crawl a page via other links on your site, it is likely that it is not inserting the authority that it could and thus is not ranking as well as it could.
If you have pages in your sitemap that are not accessible via at least one link from another page, these will be flagged as “orphaned pages in sitemaps” in your Site Audit Issues tab. It’s also mentioned in the report on Internal Linking.
92. Ensure Your Site’s Content Up to Date
Content ages and becomes out of date over time.
However, updating old content is one of the simplest tasks you can implement to see big results.
It is time well spent if the content on your page contains outdated information or could simply benefit from being brought up to date with a fresh perspective.
After all, outdated content usually does not provide the best user experience, so why would Google continue to rank it unless it is brought up to date?
93. Spread secondary/LSI keywords in Your Content
LSI keywords, also known as latent semantic indexing keywords, are synonyms or phrases that are semantically connected to your primary term.
Google debuted its Hummingbird algorithm years ago, an innovation that helps Google to understand a page’s subject by examining more than just the keywords.
LSI keywords offer context to your material, making it more relevant to wide topics. Google will then recognize that your content is of high quality and should be ranked higher in SERPs.
Use LSI keywords throughout your article to help Google bots better grasp your content, resulting in a higher page ranking.
94. Use Synonyms and LSI Keywords
Google is now intelligent. Instead of repeating a keyword 1000 times, use synonyms and LSI keywords.
Assume you want to rank for the phrase “how to start a blog.”
You’d want to include that exact keyword a few times on your page, as well as synonyms like:
- How to Start a Blog
- Creating a blog
- Starting a Blog
- How to Create a WordPress Blog
- You get the picture.
Then, include some LSI keywords. LSI Keywords are terms that are related to your primary keyword.
95. Use External Links
Make sure to include links to 5-8 authority websites in your article.
96. Use Internal Links
This is a slam dunk:
Link to 2-5 other pages on your website every time you publish new content. Internal links should have keyword-rich anchor text, according to this pro tip from Backlinko.
97. Highlight the value of your page in the metadata
Aside from being keyword-focused and ensuring that the material is encapsulated in a certain number of characters and pixels, ALWAYS remember to highlight the benefit and value of your website or content.
Will reading the material assist them in improving their performance? If they do click on your page, they will be educated on a certain topic or subject. No matter what your content’s purpose is, emphasize it because it can help users realize the value of your material merely by appearing on a SERP.
98. Use proper subheadings and Header Tags
Subheadings in your content are recommended for a better user experience. This will allow you to incorporate your keywords into your writing.
It will also make your content easier to scan. Subheadings function as roadmaps for your readers to gain an overview of your content and readily access the information they need, as many nowadays don’t have the patience to read through your article.
Remember to split your content into logical and scannable bits that your audience can readily comprehend.
Also, just as you would with your page title, remember to wrap your subheadings in the HTML code’s H2, H3, and so on tags. This will notify search engines.
99. Check that all of the links are functional
Check that all of the links are functional.
Have you ever had a faulty link or clicked on a page that took you to a poor gateway? When it comes to on-page SEO, this is a massive no-no.
Always double-check that your internal and external links are working properly and that they point to the correct pages. Don’t forget to keep them up to date, especially if they are time-sensitive, such as a limited-time offer or a holiday-only link.
Remember that a pleasant user experience is crucial, and links are part of that.
100. Have a strong call to action
Visitors to your website should know what to do after reading the content on your page. You may assist them by establishing a clear call to action.
Your call to action should be relevant to the content’s aim. For example, if the objective of your page is informational, your CTA may be “Sign Up To Learn More.”
101. Implement proper schema markup
(Photo from propelrr.com’s 28-point On-page SEO Checklist to Optimize Your Website)
Schema organizes the framework of your data so that search engines can understand it and rank it in the SERPs.
Schema.org is the product of a collaboration between Google, Bing, Yandex, and Yahoo! to assist businesses in providing information that search engines can easily interpret. This gives a shared vocabulary for webmasters and developers to use when using a schema to get the most out of their work.
“Adding Schema markup to your HTML enhances the way your page displays in SERPs by increasing the rich snippets that are displayed beneath the page title,” according to Moz.
Top search engines generally utilize three types of schema markups:
JSON-LD – Because the markup is not interleaved with the user-visible text, nested data items in JSON-LD are easier to represent.
Microdata — An open-source HTML specification that allows structured data to be nestled within HTML content.
RDFa – HTML5 extension that provides linked data by adding HTML tag characteristics that correlate to the user-visible content that you want to define for search engines.
To learn more, please visit Schema.org and the Google Structured Data Markup Helper
102. Ensure that your website can be crawled and indexed
Search engines examine, assess, and rank billions of pieces of internet content to determine which has the best chance of answering a person’s query. They accomplish this through crawling and indexing.
Crawling is the process of searching the internet for existing, new, and updated content. Crawlers or spiders are sent out by search engines to perform this. These crawlers visit a variety of web pages and follow the links on those pages to find new URLs. They discover fresh content to index as a result of this.
Of course, you can prevent crawlers from crawling and indexing your page. You can accomplish this by utilizing Robots.txt. You can also use Google Search Console and/or Screaming Frog to see whether you have any pages with a “nofollow” attribute.
103. Optimize for voice searches
Instead of entering your questions, you can use voice search by speaking to a device.
According to Forbes, “Voice search substantially enhances user experience — and as a result, by 2022, half of all internet searches will be conducted using voice search.” Because of its widespread use, search engines such as Google are emphasizing voice search optimization. “Make sure that your content satisfies the search intent of your website visitor.” If your user’s purpose is to compare and contrast two products, your information should not be focused toward generating a sale. Check out our guide to understanding search intent to be sure you’re on the correct track.
You can improve voice search results by performing the following:
- Use structured data – Enable search upgrades to receive a more visually attractive search engine results page (SERP).
- Use Google My Business listing – Share your company’s information in easy text format in the footer of your website.
- Be mobile-friendly – Because the majority of voice searches are conducted on mobile devices, it is ideal for your website to promote mobile usability and friendliness.
104. Satisfy search intent
There are four major types of search intent:
- How-Tos, tutorials, and guidelines and other kinds of informative content.
- Making a purchase or already having a product in mind.
- Comparison entails comparing several products while still assessing possibilities. For example, If you Search SEO vs SEM, or Hubspot vs Salesforce, etc.
- Navigation, which can include but is not limited to, finding a specific website or looking for a specific service.
Make certain that your content meets the search intent of your website’s visitors. If your user’s purpose is to compare and contrast two products, your information should not be focused toward generating a sale. Check out our guide to understanding search intent to be sure you’re on the correct track.
105. Write a good introduction
If you lose your readers in the introduction, you’ve lost them for good.
It is critical to write an introduction that will capture the reader’s interest in order to ensure user engagement.
To keep readers from “pogo-sticking” from page to page, catch them with a fascinating introduction that will keep them reading the entire piece. Remember that no matter how wonderful your content is, if the audience has already left at the opening, they will not be able to see it.
106. Optimize for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are organic answer boxes at the top of SERPs that search engines pull from websites in response to specific searches. It aids in the growth of organic traffic to your website.
These featured snippets are chosen from websites that rank in the top five SERPs rankings. It’s critical to remember the following while ranking and optimizing for featured snippets:
- Answer each question precisely and succinctly.
- When responding to your inquiry, use facts and data.
- Make certain that the article addresses as many related questions as feasible.
- Make sure your inquiries are correctly organized and phrased.
- To bolster your claim, include photographs, videos, or infographics.
107. Write relevant, quality, long-form content
Long-form content tends to receive more attention, both from Google and viewers. Mr. Success Online recommends that you use at least 1,000 in your content in order to increase your rank in the SERP. However, you should remember not to sacrifice content quality for length; if you create low quality content, then Google may choose not to rank you highly anyway, or viewers might learn to ignore your content after a while.
In order to keep your relevance, the subject matter in your content should be able to remain relevant for a long time, in order to keep viewers coming back.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
According to a SEMrush analysis done by Mr. Success Online, long-form content with more than 3000 words receives greater traffic, social shares, and backlinks.
Longer posts are preferable because they draw more backlinks, increasing your page’s authority and rating in SERPs. Your content should be of high quality, unique, and timely. The material you broadcast should be relevant to your search intent target category.
108. Add Social Sharing Buttons
Good material is more likely to be shared (and must be). In today’s world, where social media is used by practically everyone, information is communicated instantaneously.
By including social media sharing icons on your page, you can simply share it across many platforms, increasing traffic and brand recognition. It will also indicate to search engines that your content is informative.
Including social sharing buttons improves your customer’s experience. If your readers wish to share your blog content, providing this tool makes it more likely that they will.
109. Improve your page loading speed to 3 Seconds max
Nobody appreciates a slow-loading website, whether they admit it or not.
Make your guests happy when they visit your site by making it as fast as possible. Loading time is also used by Google as a ranking factor, so make sure to maximize your page speed. The faster your page loads, the better it ranks in search results.
110. Mobile-first indexing and responsive design
Mobile-first indexing implies that Google will most likely index and rank your page’s mobile version.
As a result, mobile-optimization of your website is a must. Furthermore, many customers use search engines on their mobile devices, so optimizing your site for smartphones and tablets can and will increase traffic and rank in SERPs.
If your website is responsively designed, it can quickly alter its layout for browsing according on the user’s device.
111. Place a reviews and comment section
(Photo from propelrr.com’s 28-point On-page SEO Checklist to Optimize Your Website)
You can also include a comment box on your sites, particularly blog pages, to communicate with your viewers and learn if they find your content beneficial.
It will also enhance dwell time on the site because users would read the comments before expressing their opinion. Don’t forget to respond to your readers’ comments!
112. Provide a good user experience (UX)
You want your website visitors to have a positive experience. Many factors contribute to a positive user experience. Here are a few examples:
- Making material that is easy to understand;
- Ensuring that all of your links are operational
- Increasing the speed with which your website loads; and
- Having a design that is mobile-friendly
It is preferred if the font type, size, and color are legible when surfing on a mobile device. Check that your website’s buttons aren’t too big or too little. If your site is difficult to navigate, your bounce rate will increase, significantly hurting your website’s performance.
113. Key Takeaways
By checking all of the boxes on our SEO on-page optimization checklist, you will be able to optimize your website for 2022. Here are some crucial points to remember when it comes to on-page SEO:
You can have low-cost marketing that can help you get a higher return on your investment (ROI).
Having an optimized website can help you generate buzz because of the particular and targeted keywords relevant to your business.
If your website has a cleaner, faster page speed, and if you use effective SEO tactics, people will be encouraged to visit it more frequently.
Off-Page SEO Checklist
You can’t ignore off-page SEO factors if you want to succeed in SEO. Despite the fact that they’re commonly referred to as “link building,” there’s more to it than that.
114. Evaluate your backlink profile
Examine your backlink profile with a tool such as Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or Moz. Examine which domains have the most links to your site, as well as which pages have the most links. Check your domain authority (DA) or domain rating (DR) for an overall backlink profile score if you use Ahrefs or Moz.
115. Paid Links: Beware the Wrath of Google
It is against Google’s webmaster guidelines to donate to charities and nonprofits in exchange for a link.
116. Don’t Build Massive Amounts of Links on Directorie
Stick to higher-quality directories that add relevance to your brand.
117. Go for Link Quality (Not Quantity)
As with content, quality over quantity applies to link building.
Link building should be strategic and targeted; it all comes down to authenticity.
118. Analyze Your Competitor’s Link Profile
How can you plan a strategy to outrank your competitors if you don’t know what their link profile looks like?
Investing time and resources into your competitor’s link profile is just as important as analyzing their content.
Analyze the link profile of any competitor by running their URL through the Backlink Analytics tool and getting a sense of the overall quality and authority of the links that point at their site.
119. Improve your internal linking
Update and improve your internal links to ensure the effectiveness of your off-page SEO strategy. Aim for three connections (with optimized anchor text) from existing pages linking to each page on your site. Screaming Frog can help you determine which pages want links, and then you can get started!
120. Conduct a Link Intersect Analysis
You may be missing out on valuable links that your competitors are utilizing. Finding quick-win opportunities can be done by conducting link intersect analysis.
Using Backlink Analytics, you can enter up to five different domains to see which domains are linking to which of your rivals.
An excellent place to begin would be to reach out and ask to be added to a resource page that links to everyone else in your field but you.
121. Fix your 404 errors
Broken links can have an influence on your user experience and off-page SEO, which is why detecting and correcting 404 errors is an important component of any off-page SEO routine. Screaming Frog will crawl your website and then work through its list of 404 issues to make your site seamless for crawlers and users.
122. Optimize your site’s on-page SEO
Off-page SEO and on-page SEO work in tandem to help your website rank high in search results.
As a result, both require your attention. If you only optimize one, your site will not attain its full potential in terms of website traffic, online leads, and money. Follow this checklist for on-page SEO and concentrate on the following practices:
- Long-tail keywords should be targeted.
- Keywords should be used to optimize title tags and meta descriptions.
- Get a good keyword density without keyword stuffing.
- Regularly publish SEO content.
- Get rid of duplicate stuff.
- Create a responsive or mobile-friendly website design
- Maintain website accessibility
- Improve page speed
- Use HTTPS for maximum website security
123. Turn Unlinked Mentions Into Links
If your PR team is successful in getting your company mentioned in the media, you may come across articles that mention your company but do not include a link to your website.
Unlinked brand mentions are what they’re called. It’s possible to quickly identify mentions of your brand that don’t link, and this guide shows you how to ask for a link when there is an existing unlinked brand mention.
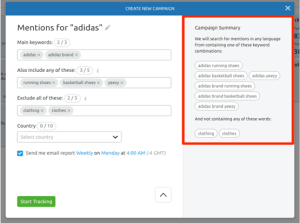
(Image from www.semrush.com/blog/seochecklist)
124. Assess your link building options
Determine which link-building methods are the most important to your organization, as well as which strategies you can implement with the time, finances, and experience you have. Concentrate your efforts on two or more methods, such as guest blogging, broken links, or sponsored advertising.
125. Steal your competition’s links with broken link building
Begin broken link construction by looking for broken external connections on sites where you’d like to earn a link, such as an industry blog. Then, look for material on your site that might be used to replace the broken link. Then, contact that website.
Repeat this process for any additional sites that are linked to the same broken link.
126. Get your content found with outreach
Outreach is another effective link-building approach, but it takes more time and effort.
The following steps are involved in this link-building strategy:
- Determine the piece of content, such as a blog post, you wish to earn a link for.
- Investigate potential blogs or websites where your content would be useful.
- Pitch the writer, editor, or webmaster on the possibility of sharing or connecting to your content.
Consider studying blogs and subjects before generating material for the best results with this method. Rather than trying to discover a perspective for current content, this technique might help you organize content that bloggers will already want.
127. Find New Link Building Opportunities
You can always find new ways to build links, but it can take some time to find them. Use the right SEO tools to make the process of building a strong backlink profile easier.
Using the Link Building Tool, for example, you can see a constant stream of new opportunities and websites that you can reach out to. In just a few minutes, you’ll have access to a slew of new opportunities and a solid strategy for gaining a significant advantage over your rivals.
128. Set Up and Optimize Google Business Profile
Even though links are a major ranking factor, off-page factors go far beyond that.
Ensure that your local business is listed on Google’s Business Profile if you have one (GBP). If you don’t, you’ll be handing visitors over to a rival.
It is undeniable that optimizing and maintaining your GBP listing to an acceptable standard takes time. The time you spend here will benefit you regardless of whether you serve customers at their location or they come to you.
129. Promote your content with paid ads
Advertise on ad networks such as Google Ads and Facebook to promote your content. Lead gen items such as an infographic, tool, or research study, etc, (which the user obtains by submitting their email address, phone number, or some other way to contact them) can generate traffic to your website. Get the most out of this off-page optimization checklist item by monitoring and improving ad campaigns on a regular basis.
130. Share your knowledge (and site) with guest blogging
Guest blogging is an additional beneficial, albeit optional, element to your off-site SEO checklist. Guest blogging can be broken down into the following steps:
- Make a list of industry websites that welcome guest bloggers or third-party articles.
- Examine the content, tone, and audience of each website.
- Create a list of content subjects that correspond to the blog’s brand, audience, and needs.
- Pitch one of your subjects to the site’s webmaster or editor.
If your idea is approved, you will begin writing and revising the material. Depending on the blog, your post may include an author biography as well as a link to your website. Some blogs, on the other hand, will designate this link as nofollow, instructing crawlers not to follow it.
In either case, blogging on another website exposes your brand to a new audience. You can probably include links back to your website into your material over time (and when appropriate).
131. Post your content on social media
Social media provides a free platform for your company to share content.
If you want to maximize the effectiveness of this link-building approach and off-page SEO checklist, you should devote some time to social media marketing and social media advertising. These two strategies can assist you in increasing your online following, which can lead to additional shares and backlinks. Because of social media algorithms, it is difficult for businesses to build an online social media following.
Most algorithms now favor content from a user’s friends over content from businesses that the user follows. As a result, many brands promote on social media and boost organic posts, such as those on Facebook.
Content Checklist
There’s no way around it: great content is essential if you want to be found on Google. The reason for this is that content is now an essential part of any modern-day search engine optimization strategy. I’ll walk you through the process of creating content that will be relevant in the year 2022 and beyond in this section (and beyond).
132. Write About Topics (Not Keywords)
To better align your content with the intent of your audience, write about topics rather than keywords. You can, and should, include these keywords of course, but you need to write something people will want to read, and try to fit your keywords into it in a way that will feel natural to the reader.
133. Get Rid of Thin Content (or Rewrite it)
It does nothing but degrade the quality of your site.
Long-form content has been shown to rank higher in search results (though this does not always guarantee success).
134. Clean up Duplicate Content
By cleaning up duplicate content, you are removing any scraped or duplicate content from your site. If you find duplicate content on other sites, email the webmaster and request that it be removed, or add it to your disavow file.
135. Check Your Old Content
Sometimes old content continues to drive traffic.
If this is the case, consider writing a new post with similar content to generate new, fresh, and more relevant content.
136. Syndicate Your Content
If you’re using syndicated content, make sure the other site includes the rel=canonical tag to link back to your original page.
137. Content Repurposing
This is not a novel concept, but it is frequently overlooked.
Consider how each piece of content you create can be repurposed as a video, Facebook Live, Slideshare, and so on.
138. Edit! Edit! Edit!
When creating content, double-check your spelling, grammar, and consistency.
Errors will not affect your rankings, but they will degrade the user experience and harm your credibility.
139. Use Tools to Generate Content Ideas
Use tools like BuzzSumo to reverse engineer your competitors’ top-performing content when deciding what type of content to write, but remember not to outright copy them.
140. Check the Cache
When working with influencers or having your content posted on another site, do a quick search for “cache: URL” to see when their pages were last cached.
Save your content for somewhere else if it’s more than a month old.
141. Write Conversationally
To rank for voice search queries, create content in a conversational tone.
142. Write Original Product Descriptions
Take the time to write unique product descriptions for users and search engines if you run an ecommerce site.
Duplicating manufacturer content can harm your rankings and drive users away.
143. Test Your Meta Descriptions
If your impressions are increasing but your clicks are decreasing in Google Search Console, try A/B testing (a type of Split-run testing for UX) your meta description copy to see what can increase clicks. Making the Meta description as close to a search query is the best, but sometimes the way things are phrased can be more enticing than others. Testing a description for a week on a top page for a week at a time to find what provides the most click throughs is a good first step.
Google does have a self-rewarding system where the more clicks something has, the more relevant and more it will want to show it. So by capitalizing on this element, you can continue to drive your rankings and traffic up.
144. Eliminate Keyword Cannibalization
To avoid cannibalization, combine content from multiple pages competing for similar keyword search terms into one massive piece of long-form content.
145. Analyze Your Content
Are you wondering why your competitor is outranking you in the SERPs for the same piece of content?
Return to your content and fill in the blanks.
Analyze the keyword terms related to your article to see if there are any missing pieces that can be added to beef up your content.
146. Personalize the User Experience
Different content should be served to new and returning visitors.
147. Create Amazing Content Using “The Skyscraper Technique”
Using the Skyscraper Method, you can quickly and easily create eye-catching content.
Here are the three steps:
In the first place, find a piece of content that is already popular in your field, second, find a way to improve on it, and third, spread the word about the information you’ve created by reaching out to site owners who have already shared or linked similar content, and ask that they share yours.
When it comes to learning more about The Skyscraper Method, there are two helpful resources:
My All-Time Favorite White Hat SEO Technique (59% More Organic Traffic)
How I Increased My Search Traffic by 110% in 14 Days
148. Chunk Your Content to Maximize Readability
Breaking content into manageable chunks is always preferable to reading long walls of text.
149. Cover Your Page’s Topic In-Depth
One thing stood out when Backlinko analyzed over 11 million Google search results:
The best content on Google tends to be comprehensive.
Comprehensive meaning it is deep and high value content, exceeding 1500 words, and even up to 5000+ words.
150. Focus on Content Formats That Are Working Right Now
Sites that have established a solid reputation for providing unique, authoritative content stand to benefit the most from this shift.
Original and authoritative content: what does that mean?
- Content penned by professionals
- Use first-hand findings (like surveys and industry studies)
- Case studies and real-life examples of content that goes beyond regurgitated data
- Content that can be relied upon for a long time
151. Use Multimedia
There are two main reasons I do this:
First and foremost, it improves the quality of the content.
Second, images and other forms of multimedia aid in the ranking of content.
If you want to incorporate multimedia into your content, We recommend the following:
- Videos (add a description)
- Carousels
- Images (with alt text)
Remember that adding descriptions and/or alt text helps the search engine properly identify the content of the media.
Local SEO Checklist
152. Focus on Facts & Local Guides
With the rise of digital assistants such as Google Home, Amazon Echo, and others, content centered on facts and local guides will be beneficial for brands looking to rank first.
153. Create Travel Guides
Make use of Google’s Knowledge Graph’s trip planning feature.
If you own a local business or a travel agency, creating travel guides may benefit you.
154. Use Google Local Inventory Ads
If you use Google’s Local Inventory Ad program, customers can browse your local store through Google.
155. Collect More Reviews
Implement strategies to boost reviews for your local business.
The vast majority of customers read reviews for local businesses, and the ones with the most reviews are prioritized.
156. Optimize for Geographic Regions & User Locations
If you own a physical store, use Google Ads distance and store visit reports to determine which geographic regions and user locations are driving the most in-store purchases.
157. Optimize for Multiple Locations
If you have multiple locations, make sure the name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across all of your local profiles.
158. Utilize Regional Pages
Utilize regional pages if your locations are spread out across several states.
159. Include Photos on Your Local Pages
Interior design can help your business look more appealing to customers.
160. Optimize your website for “near me” searches.
The use of location-based voice search queries has increased.
Consider incorporating phrases like “near me” into your content and advertising strategy.
Special Google Algorithms
161. Query Deserves Freshness
Google prioritizes the latest pages for certain search queries.
162. Query Deserves Diversity
For ambiguous keywords like “Ted,” “WWF,” or “ruby,” Google may add a broader range of results to the SERP in hopes of finding something relevant to your search intent.
163. User Browsing History
You’ve probably noticed that online sites you visit frequently receive a SERP boost for your searches.
164. User Search History
Previous searches influence search results for subsequent searches. For instance, if you search for “reviews” and then “toasters,” Google is more likely to rank toaster review sites higher in the SERPs than it would toaster retail sites based on the AI’s assumption that searching the word “reviews” indicates that you would be interested for reviews on whatever you search for, even if you didn’t include it in your current search.
165. Featured Snippets
Google chooses Featured Snippets content based on a combination of content length, formatting, page authority, and HTTPs usage, according to a SEMRush study.
166. Geo targeting
Google prioritizes sites with a local server IP address and a country-specific domain name extension.
167. Safe Search
People who have Safe Search enabled will not see search results containing curse words or adult content.
168. “YMYL” Keywords
Google has stricter content quality standards for “Your Money or Your Life” keywords.
169. DMCA Complaints
Pages with legitimate DMCA complaints are “down ranked” by Google.
170. Domain Diversity
The so-called “Bigfoot Update” allegedly increased the number of domains on each SERP page.
171. Transactional Searches
Google occasionally returns different results for shopping-related keywords, such as flight searches.
(Image from Google Search)
172. Local Searches
For local searches, Google frequently prioritizes local results over “normal” organic SERPs.
173. Top Stories box
The following keywords cause a Top Stories box to appear:
- News
- Recent News
- Top Stories
- News Stories
- Etc.
174. Big Brand Preference
Following the Vince Update, Google began favoring big brands for specific keywords.
175. Shopping Results
Google displays Google Shopping results in organic SERPs on occasion.
176. Image Results
Google images occasionally appear in regular, organic search results.
177. Easter Egg Results
Google returns about a dozen Easter Egg results. When you search for “Atari Breakout” in Google image search, for example, the search results transform into a playable game (!). Victor Pan deserves credit for this one.
This can be brand dependent but Google does reward these novel and higher levels of customer experience.
178. Results from a Single Site for Brands
Domain or brand-related keywords produce multiple results from the same site.
179. Update on Payday Loans
This is a special algorithm designed to clean up “very spammy queries.”
Brand Signals
180. Branded Anchor Text
Branded anchor text is a simple — but powerful — brand signal, while a plain link is ugly. Which would you rather insert into your article?
This: https://accelerateagency.ai/anchor-text
Or this: Accelerate Agency: What is Anchor Text?
Luckily, many links now automatically format as an anchor text when pasted, but not all of them are.
181. Branded Searches
People look for brands. When people search for your brand on Google, it shows Google that your site is a legitimate brand.
182. Brand + Keyword Searches
Do people search for a specific keyword along with your brand (for example, “Backlinko Google ranking factors” or “Backlinko SEO”)? If this is the case, Google may give you a ranking boost when people search for the non-branded version of that keyword in Google.
183. Having a Lot of Likes on Facebook
Having a lot of likes on Facebook is one factor that helps convince Google that your website should be near the top of the SERP
184. Twitter Profile with Followers
A Twitter profile with a large number of followers indicates a popular brand.
185. Official Linkedin Company Page
The majority of legitimate businesses have company Linkedin pages. Having one adds to your credibility.
186. Social Media Account Legitimacy
A social media account with 10,000 followers and only two posts is likely to be interpreted very differently than another 10,000-follower account with a lot of interaction. In fact, Google applied for a patent for an system to determine whether social media accounts were real or fake.
Having legimately good Social Media engagements and interactions can and will increase the SEO value in direct and indirect ways.
187. Brand Mentions on Top Stories
Very large brands are frequently mentioned on Top Stories sites. On the first page, some brands even have a feed of news from their own website.
188. Brick and Mortar Location
Real businesses have physical locations. It’s possible that Google looks for location data to determine whether or not a site is well-known.
Social Media Checklist
189. Use Twitter Cards
To make your URLs more clickable, replace your Twitter URL with Twitter Cards.
190. Use Facebook Open Graph Tags
You want to include Open Graph markup to improve how your Facebook posts are seen.
191. Don’t Just Work on Your Personal Profile on LinkedIn
Work on your company’s profile as well. Companies with more complete profiles get more views.
192. Join Instagram
If your e-commerce business isn’t already on Instagram, now is the time to start.
Instagram (and Facebook) are introducing features that allow users to shop directly from the app.
193. Invest in Customer Service on Facebook
Chatbots and automated messages transform this into an effective extension of your customer support team.
194. Experiment with LinkedIn Ads.
LinkedIn allows you to track conversions to see how many users are converting from your sponsored content and ads.
195. Make use of Facebook Playlists.
New features make it easier to create and interact with Facebook playlists.
Test them out.
196. Make use of Pinterest’s Shop the Look Ads.
Pinterest, like Google Ads, has added “Shop the Look” ads, which are ads that, when you click on them, will have similar items to whatever appears in the photo you selected.
It can be used to convert more mobile searchers.
197. Explore Reddit
Reddit is the seventh most popular website in the United States and appearing on Reddit can increase traffic going through your website.
You can begin by experimenting with their sponsored content ads.
198. Facebook Geotargeting
Geotarget your Facebook Live posts to include or exclude specific locations if you’re a local business on Facebook.
199. Always Sign a Contract
Always have a contract in place when working with an influencer. You should understand what the influencer expects from you and vice versa.
200. Be Engaged
Pursuing social bookmarks as part of your SEO strategy is a waste of time.
Instead, concentrate on earning links and engaging in social bookmarking platforms in the same way that you would on social media.
You must engage in a conversation, leave a few comments, or upvote non-related content.
Be sure to check out our SEO checklist for your 2022 SEO maintenance.
If you need any help on your own website, feel free to reach out to us here.







